Breast Development in Transwomen: Comprehensive Guide
Share
Disclaimer:
This article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Individuals considering hormone therapy, surgery, or any other intervention should consult a qualified healthcare professional.
Introduction
Breast development is an important part of gender affirmation for many male-to-female (MTF) transgender individuals. The process typically involves hormonal, physiological, and surgical factors that influence how breast tissue forms and matures. Understanding the role of hormone replacement therapy (HRT), genetic influences, and available enhancement options can help individuals make informed decisions in consultation with healthcare professionals. This article provides an overview of current knowledge on breast development in trans women, emphasizing scientific and educational context rather than clinical guidance.

What Does HRT Do in Male-to-Female Transition?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) plays a central role in the physical feminization process. HRT typically involves introducing estrogen and anti-androgen medications, which together suppress testosterone and encourage changes that align more closely with female secondary sex characteristics.
Common physiological changes observed during HRT include:
-
Breast tissue formation: Development of breast buds and gradual enlargement.
-
Redistribution of body fat: Fat moves toward the hips and thighs in a typically feminine pattern.
-
Reduced muscle mass: Muscles become softer and less pronounced.
-
Skin changes: Texture becomes smoother and less oily.
-
Hair growth reduction: Body hair growth slows and becomes finer.
These effects vary widely among individuals depending on genetics, age, dosage, and duration of therapy.
Psychological and Social Considerations
The effects of HRT extend beyond physical appearance. Studies from institutions such as UCSF Transgender Care and the Endocrine Society have shown that many transgender women experience improved psychological well-being as their physical characteristics become more congruent with their gender identity. This alignment often supports greater self-esteem and reduced gender dysphoria.
Access to mental-health support and affirming care providers can be critical for maintaining overall well-being throughout this process.
General Risks and Monitoring
Published clinical guidelines (such as those from the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH)) emphasize that hormone therapy requires appropriate medical supervision. Monitoring typically includes periodic evaluation of hormone levels and general health to ensure safe administration.
Potential risks reported in medical literature include cardiovascular events, blood-clot formation, and metabolic changes. The likelihood of these risks varies depending on age, medical history, and mode of estrogen delivery. This article does not offer clinical recommendations but encourages readers to review credible health resources and discuss options with licensed professionals.
Methods of Hormone Administration
Estrogen therapy can be delivered in several forms, each with advantages and considerations documented in medical literature:
-
Oral estrogen (tablets)
-
Transdermal estrogen (patches or gels)
-
Injectable estrogen (intramuscular or subcutaneous injections)
Different delivery methods influence hormone levels, convenience, and side-effect profiles. Clinical practice guidelines from the Endocrine Society (2017) note that no single route is universally superior; suitability depends on individual factors evaluated by healthcare providers.
Factors Influencing Breast Development

The extent of breast development during HRT varies widely. Research highlights several influencing factors:
-
Genetics: Family history of breast tissue density and size.
-
Age: Younger individuals tend to exhibit stronger tissue response.
-
Body mass index (BMI): Adequate nutrition and body fat levels may affect visible growth.
-
Duration of therapy: Development often progresses over two to three years before stabilizing.
-
Hormone regimen: Type, dosage, and consistency of hormone use.
While HRT initiates genuine breast tissue growth, the outcome differs from person to person. Most trans women achieve some degree of breast enlargement, but not all reach the size they desire through hormones alone.
Preparation and Support
Before beginning hormone therapy, many individuals undergo baseline assessments—not as a prescriptive step but as a common medical practice reported in guidelines. These assessments help evaluate general health and suitability for treatment.
Psychological preparation is also important. Support groups, counseling, and community resources allow trans women to share experiences and build resilience during transition.
A balanced lifestyle—adequate sleep, nutrition, and regular movement—can contribute to overall well-being, though specific routines should be individualized.
Breast Growth Patterns Observed During HRT
The biological stages of breast development in trans women parallel those seen in cisgender puberty:
-
Initial budding – Formation of breast buds under the areola.
-
Growth phase – Gradual enlargement of glandular and fatty tissue.
-
Stabilization – Slower growth, typically after two to three years.
Peer-reviewed studies note that the final cup size achieved through HRT alone may be modest, though outcomes are highly individualized.
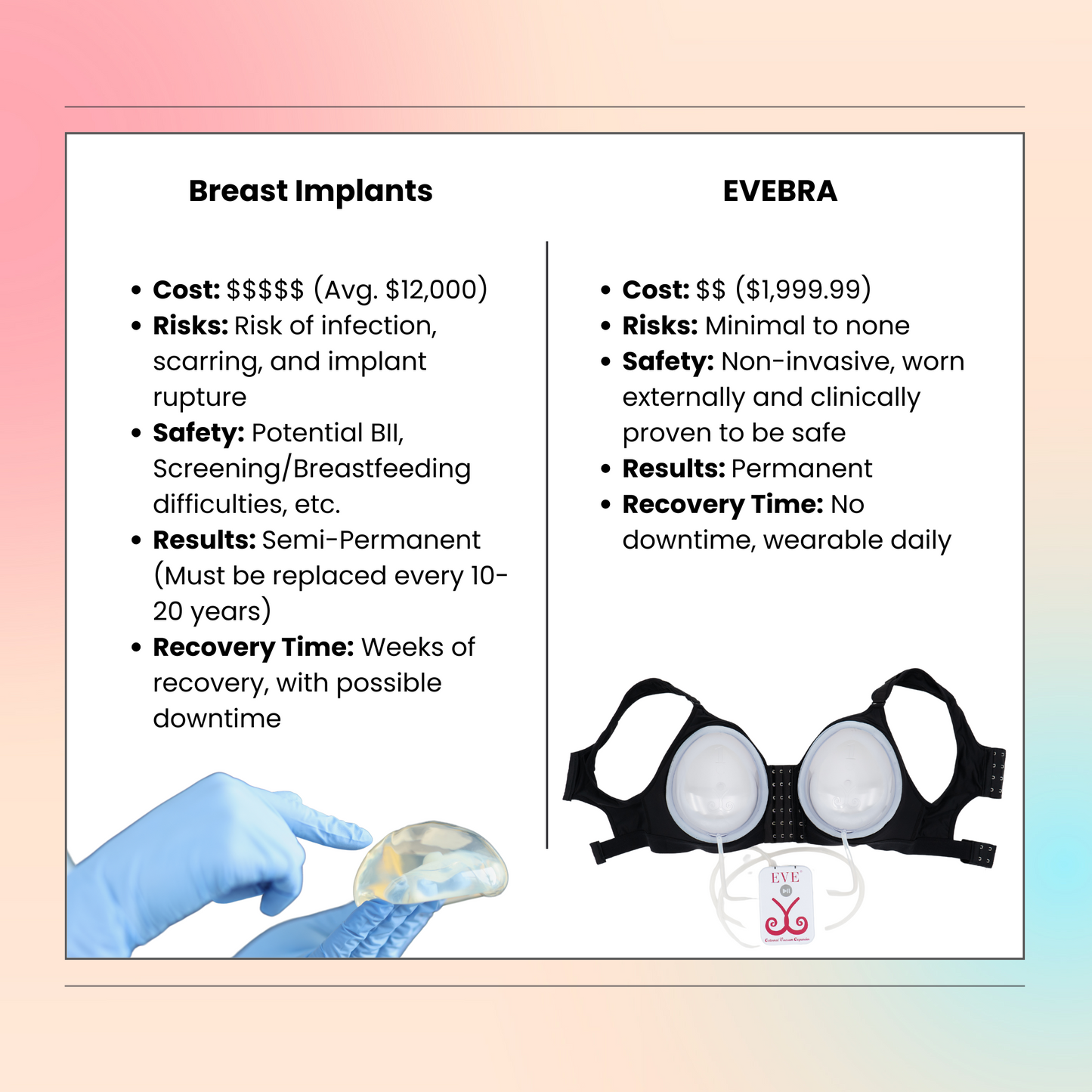
Surgical Breast Enhancement
When HRT alone does not meet a person’s aesthetic goals, surgical breast augmentation may be considered. Academic sources such as the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) describe available techniques including:
-
Implant augmentation using silicone or saline implants.
-
Autologous fat transfer, where one’s own body fat is injected to enhance volume.
The decision to pursue surgery is personal and multifaceted, encompassing physical, financial, and emotional considerations. Patients generally discuss options, risks, and expected results with board-certified surgeons specializing in gender-affirming care.
Non-Surgical Breast Enhancement: Educational Overview
Some individuals explore non-surgical approaches to breast enhancement. These methods typically aim to promote gradual tissue expansion or provide a temporary aesthetic effect without surgical intervention.
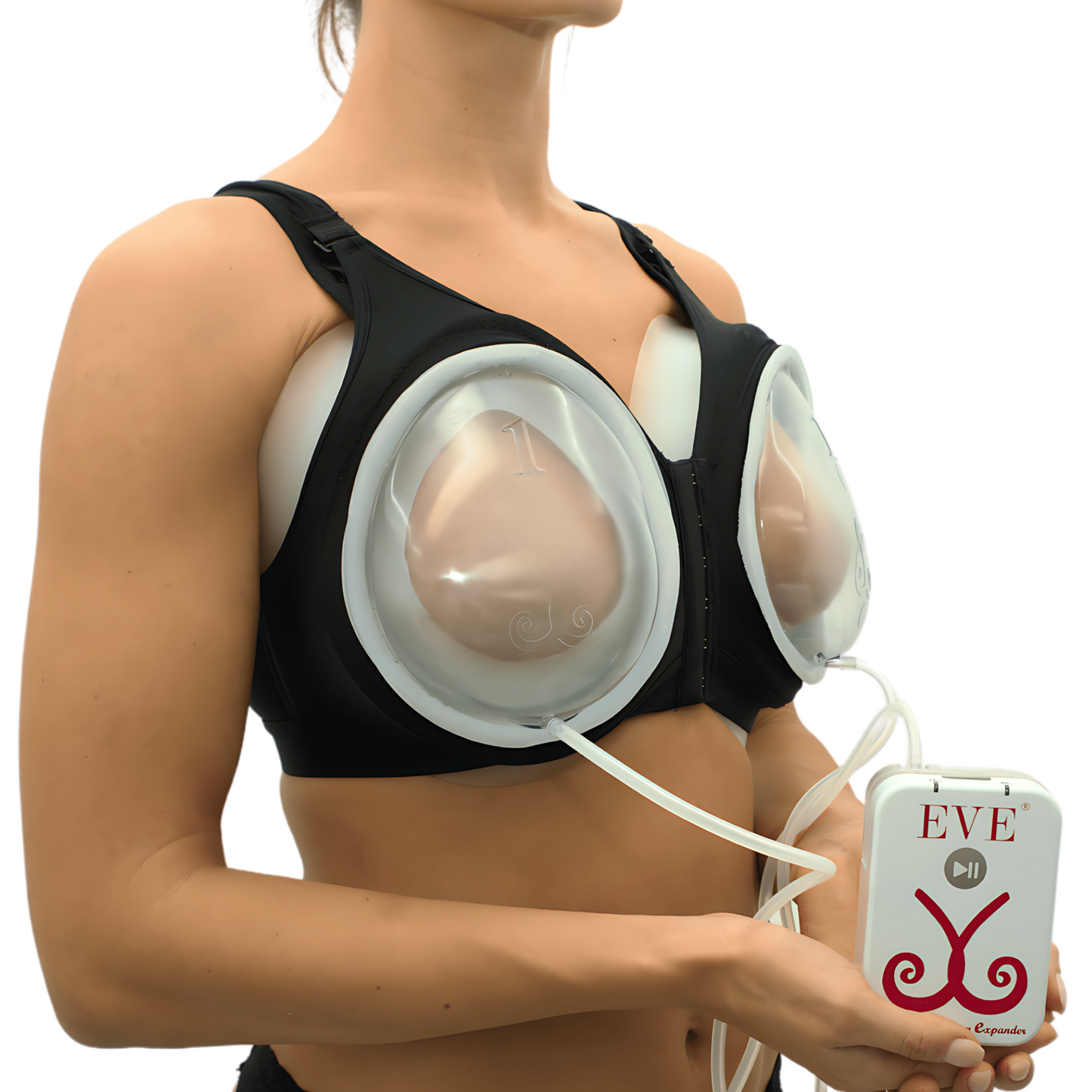
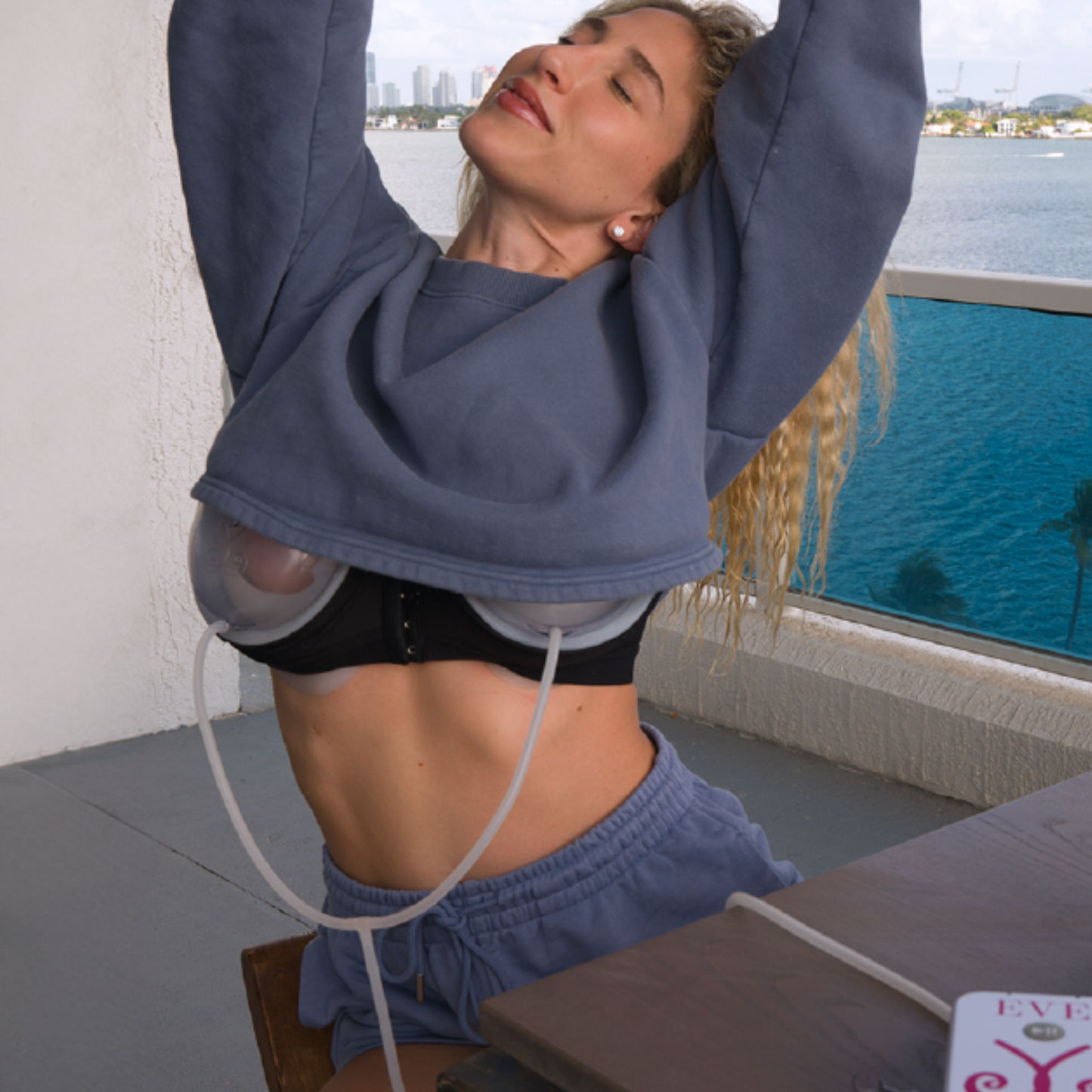
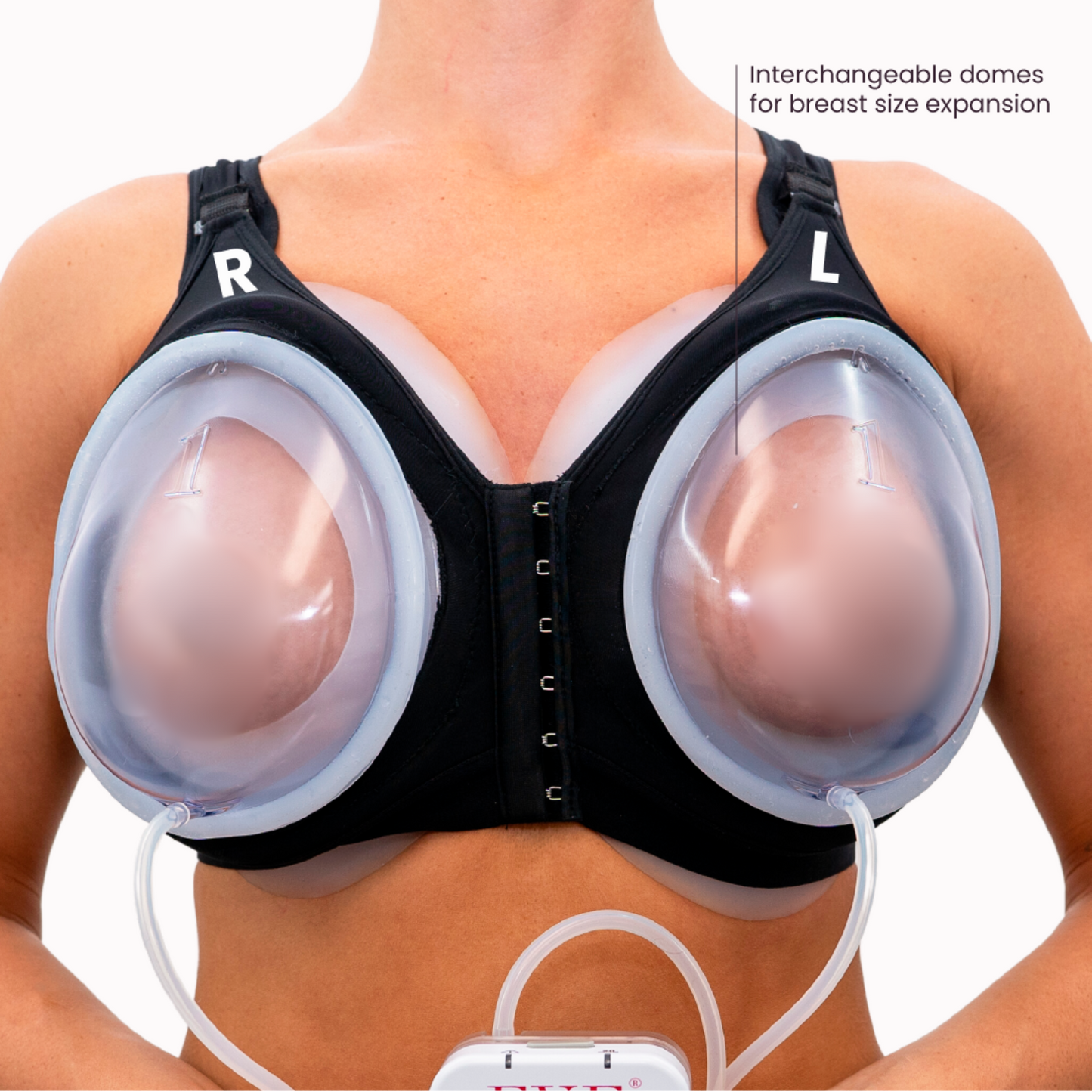
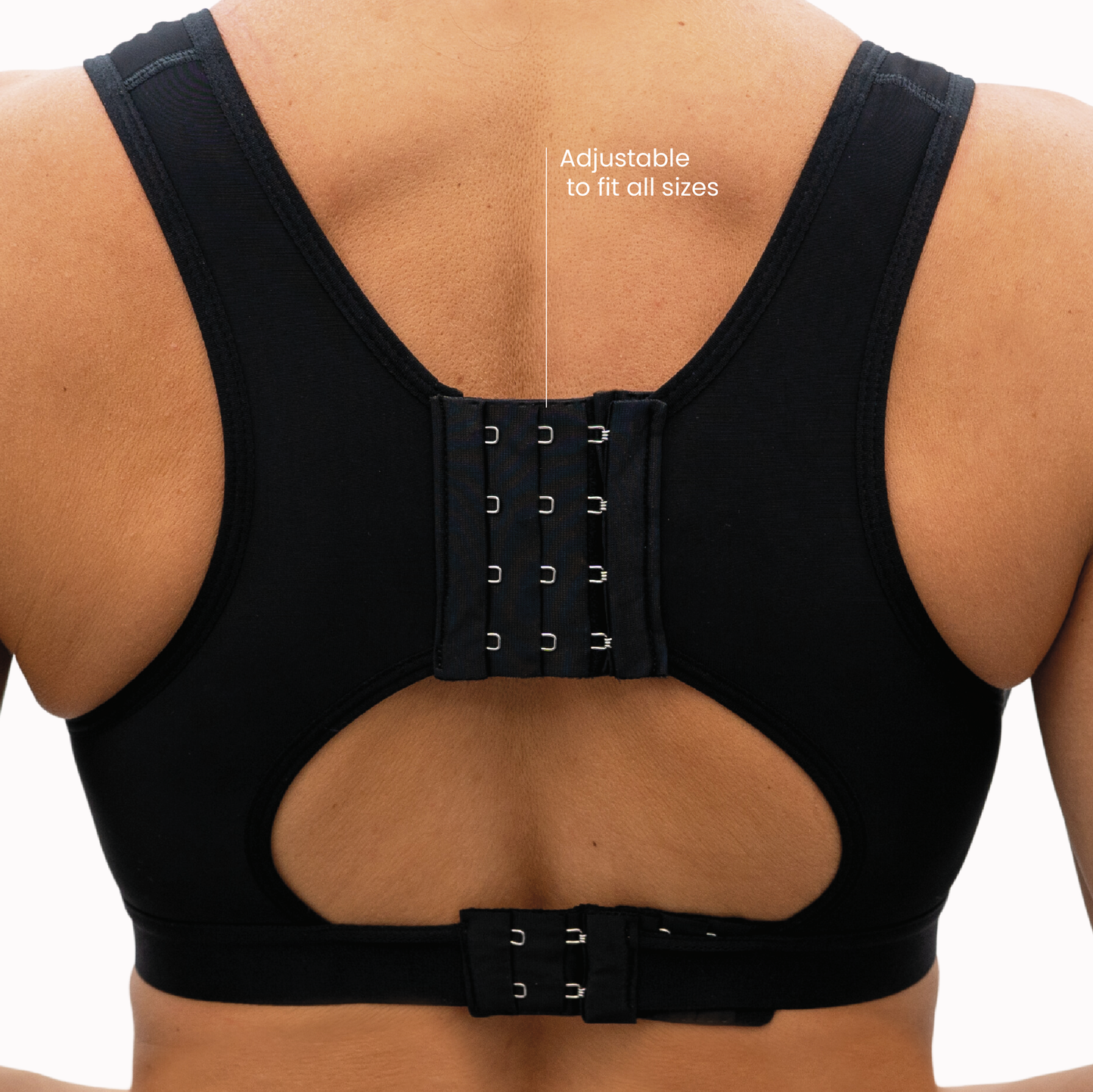
One example of this approach is the EVEBRA system, which utilizes an external, vacuum-based mechanism that gently applies consistent tension to the breast area. The principle behind this method—known in reconstructive research as tension-induced tissue growth—has been discussed in medical literature (Khouri et al., Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2000).
EVEBRA represents a continuation of earlier soft-tissue expansion technology, redesigned for comfort and modern usability. Many reports describe visible changes after several months of consistent use. The device is positioned as a non-surgical option for those interested in exploring gradual, mechanical breast tissue expansion.
Genetics and Realistic Expectations
Genetic background plays a major role in determining breast size, shape, and tissue density. Understanding these influences can help set realistic expectations. Research indicates that while hormones and mechanical expansion can stimulate tissue growth, genetics ultimately define the upper range of achievable development.
Educational resources from WPATH and UCSF emphasize the importance of individualized expectations and ongoing psychological support to ensure positive self-image throughout the transition process.
Alternatives to Surgery
For those who do not wish to pursue surgical procedures, other options may help achieve a desired silhouette or sense of affirmation, such as:
-
Padded bras or external prosthetics, which provide immediate aesthetic enhancement.
-
Hormone therapy alone, which often yields moderate natural breast growth.
-
External expansion devices like the Evebra system, offering gradual change.
These approaches differ in permanence and comfort but may each play a role depending on personal goals.
Community, Advocacy, and Support
Community networks are a cornerstone of transgender well-being. Connecting with others—whether online or in person—provides valuable emotional and informational support. LGBTQ+ centers, peer groups, and advocacy organizations offer education on healthcare access, rights, and affirming resources.
Professional counseling can also help address emotional challenges that may arise during transition, supporting resilience and mental health.
Legal and Ethical Context
Access to gender-affirming care, including HRT and surgical procedures, remains subject to varying legal frameworks worldwide. Understanding patient rights and available protections helps ensure informed, ethical, and compassionate care. Advocacy organizations continue to work toward expanding inclusive healthcare policies.
Conclusion
Breast development in trans women is a multifactorial process influenced by hormones, genetics, lifestyle, and available medical technologies. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) initiates natural changes in breast tissue, while surgical and non-surgical options can further enhance results for those who choose them.
This educational guide summarizes current understanding and highlights the importance of informed decision-making in collaboration with qualified healthcare professionals. Every journey is unique, and outcomes depend on many biological and personal factors.
FAQ (Educational Overview)
What is the role of HRT in breast development?
HRT introduces estrogen and reduces testosterone, promoting the growth of breast tissue and other feminizing changes. Individual outcomes depend on many variables including genetics and duration of treatment.
How long does breast development typically take?
Visible changes often begin within months and can continue for several years. Growth usually stabilizes after two to three years, though minor changes may persist longer.
Can all trans women achieve their desired size with HRT alone?
Not always. While many experience meaningful development, others may pursue surgical or non-surgical methods for additional enhancement.
What non-surgical options exist?
Some external expansion systems, such as vacuum-based devices, aim to encourage gradual growth through sustained tension on breast tissue. Effectiveness and comfort vary by user.
Is breast augmentation surgery common among trans women?
Yes, it is one of the most frequent gender-affirming procedures. Techniques and outcomes differ based on anatomy, implant type, and surgeon expertise.
Are regular screenings important after breast development?
Health organizations recommend routine breast health monitoring based on individual risk factors and medical history. Screening schedules should be established with a qualified clinician.
Can breast development reverse if HRT stops?
Partial regression is possible if hormone therapy is discontinued, but developed glandular tissue often remains. Decisions about continuing or stopping HRT should always be made under professional supervision.
References
-
World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH). Standards of Care for the Health of Transsexual, Transgender, and Gender Non-Conforming People, Version 7.
-
Mayo Clinic. Hormone Therapy for Transgender Individuals.
-
UCSF Transgender Care. Guidelines for the Primary and Gender-Affirming Care of Transgender and Gender Nonbinary People.
-
Endocrine Society (2017). Clinical Practice Guidelines for Endocrine Treatment of Gender-Dysphoric/Gender-Incongruent Persons.
-
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). Breast Augmentation for Transgender Women.
-
Khouri, R. K., et al. (2000). Nonsurgical Breast Enlargement Using an External Soft-Tissue Expansion System. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 105(7), 2500-2512.
-
Breastcancer.org. Breast Cancer Risk in Transgender People.
Disclaimer:
The information presented here is for educational use only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from qualified healthcare providers regarding hormone therapy, surgery, or other medical decisions.