Breast Augmentation in Transgender Patients
Share
Breast augmentation is a very significant medical and gender affirming procedure for many transgender women. This article explores various aspects of breast augmentation, particularly highlighting the innovative EVEBRA device.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Breast Augmentation
- Understanding Transgender Breast Augmentation
- Role of Hormone Therapy in Breast Development
- EVEBRA: A Revolutionary Device For Breast Augmentation
- Types of Breast Implants For Surgical Breast Augmentation Patients
- Preparing for MTF Breast Augmentation Surgery
- The Silicone or Saline Implants Surgical Procedure
- Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
- Potential Risks and Complications
- Achieving Desired Breast Size and Shape
- Psychological and Emotional Considerations
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure aimed at increasing breast size and improving breast shape. It involves the placement of breast implants or the use of fat grafting techniques. This cosmetic procedure is is commonly sought by transgender women as part of their gender affirmation journey.
Breast augmentation helps transgender patients achieve a feminine breast shape, alleviating gender dysphoria and enhancing their overall well-being. The procedure typically involves silicone or saline breast implants, each offering distinct benefits. Silicone breast implants provide a more natural feel, while saline breast implants can be adjusted for size during surgery.
Hormone therapy is often a precursor to breast augmentation surgery. Estrogen therapy stimulates breast tissue growth, contributing to a more natural appearance post-surgery. However, many transgender women may have hormonal therapy and still seek surgical enhancement to achieve their desired breast size and shape.

2. Understanding Transgender Breast Augmentation
Transgender breast augmentation, or male-to-female (MTF) breast augmentation, is designed from male to female to create a more feminine breast shape and size. This surgery is often performed after hormone therapy, which plays a crucial role in developing breast tissue.
Transgender patients may experience minimal breast tissue growth with hormone therapy alone, necessitating surgical intervention to maximize breast growth. Breast feminization surgery aims to address these challenges, providing transgender women with the desired breast projection and shape. The choice of breast implant size and type is critical to achieving a harmonious and proportionate appearance.

3. Role of Hormone Therapy in Breast Development
Hormone therapy, particularly estrogen, is essential for transgender women undergoing breast augmentation. It promotes breast tissue growth and helps trans women achieve a more natural breast appearance. Hormone therapy is usually initiated before surgery and continues postoperatively.
In addition to estrogen, anti-androgens are often prescribed to suppress testosterone levels, further facilitating breast development. The duration and effectiveness of hormone therapy can vary among individuals, making personalized treatment plans crucial for optimal outcomes. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor hormone levels and adjust therapy as needed.
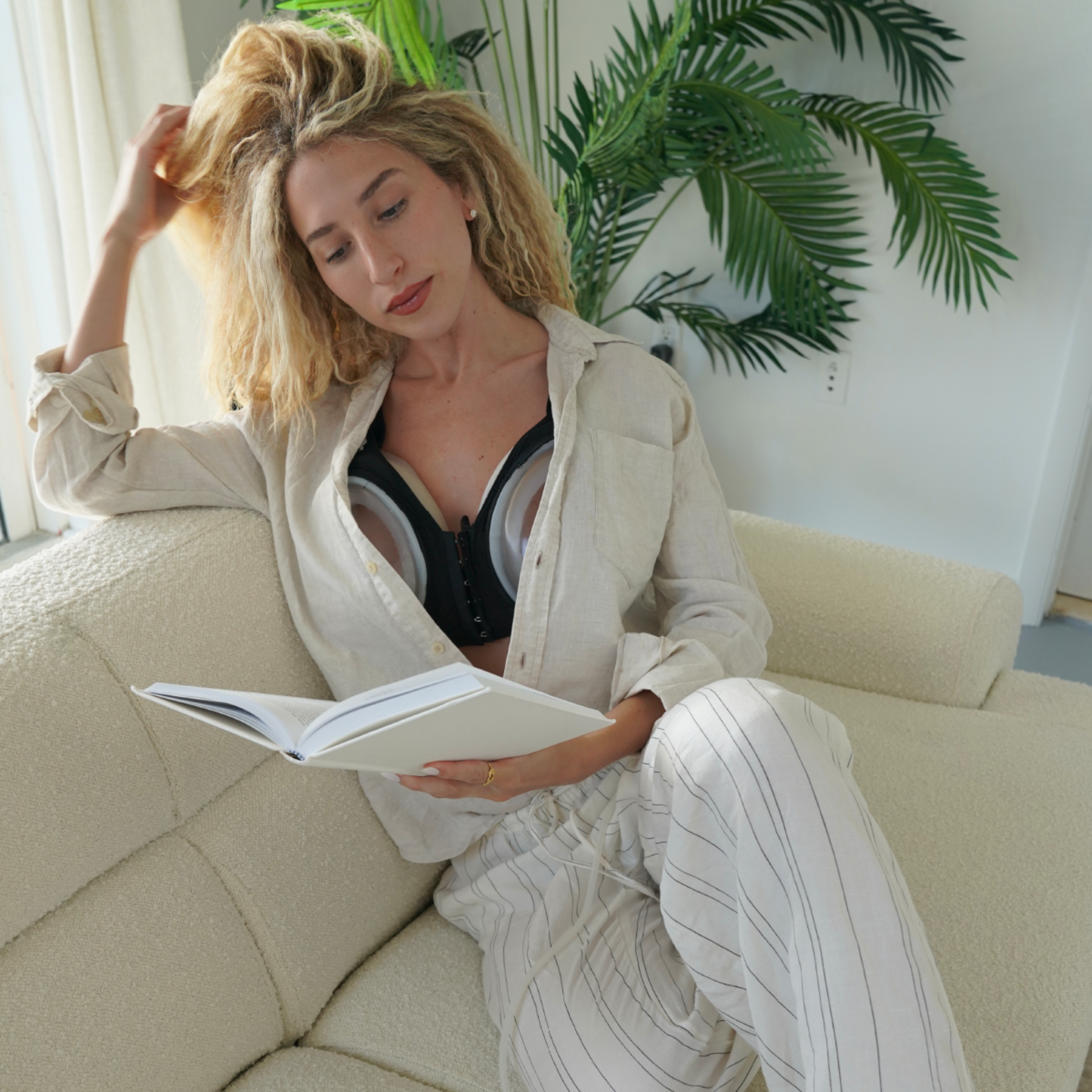
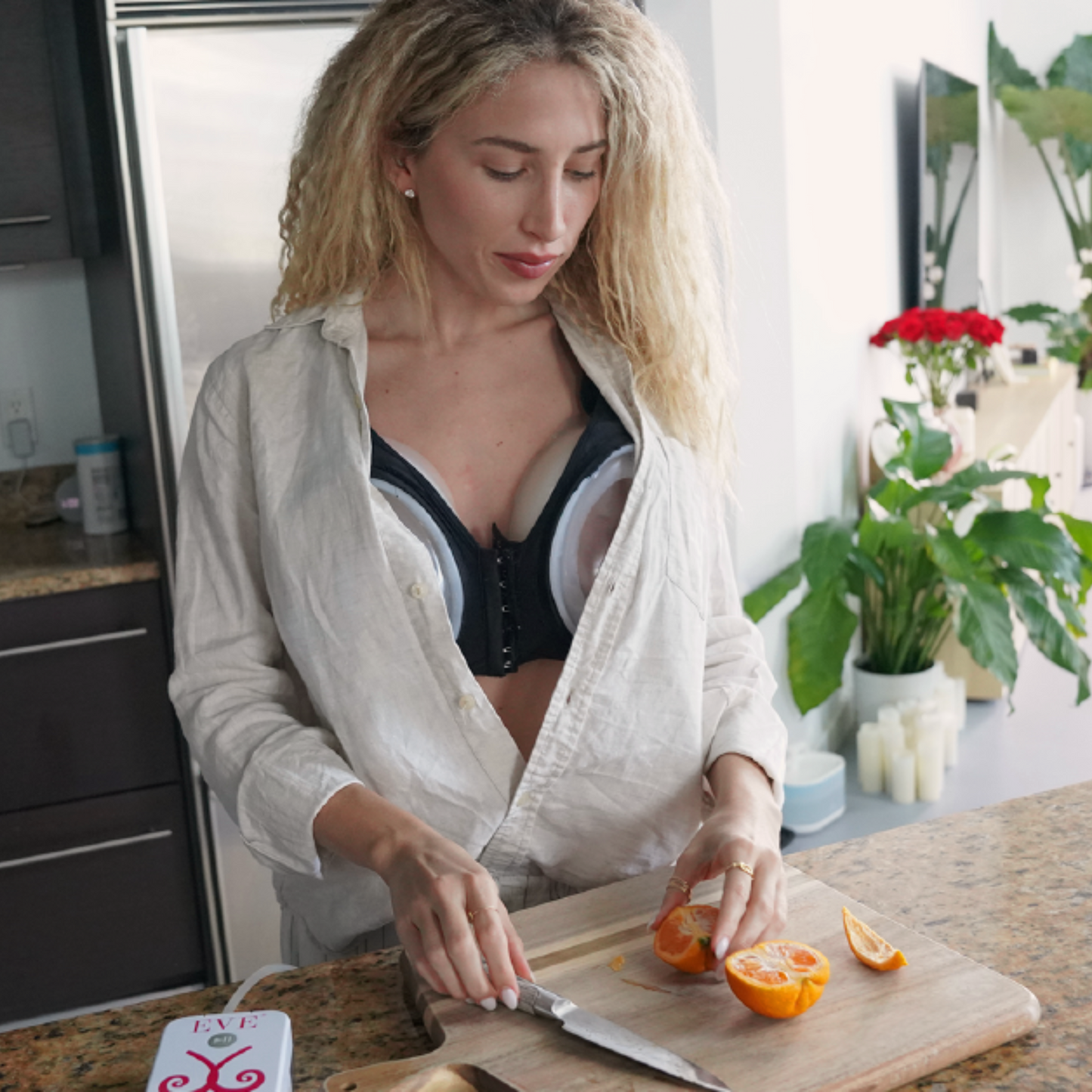
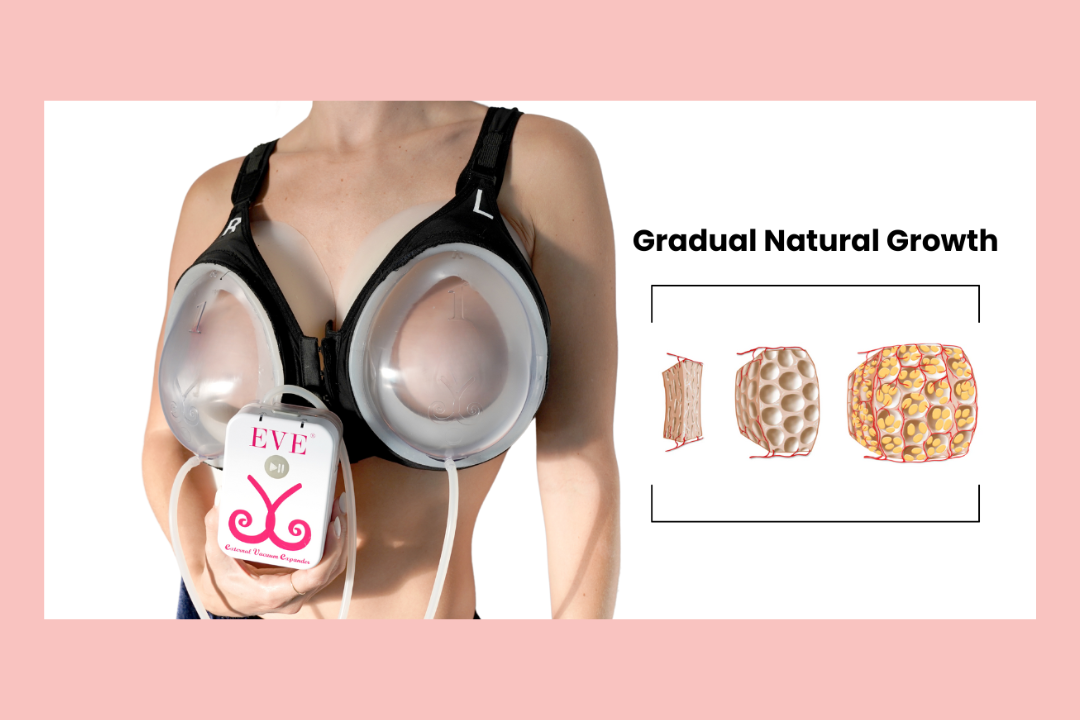
4. EVEBRA: A Revolutionary Device For Breast Augmentation
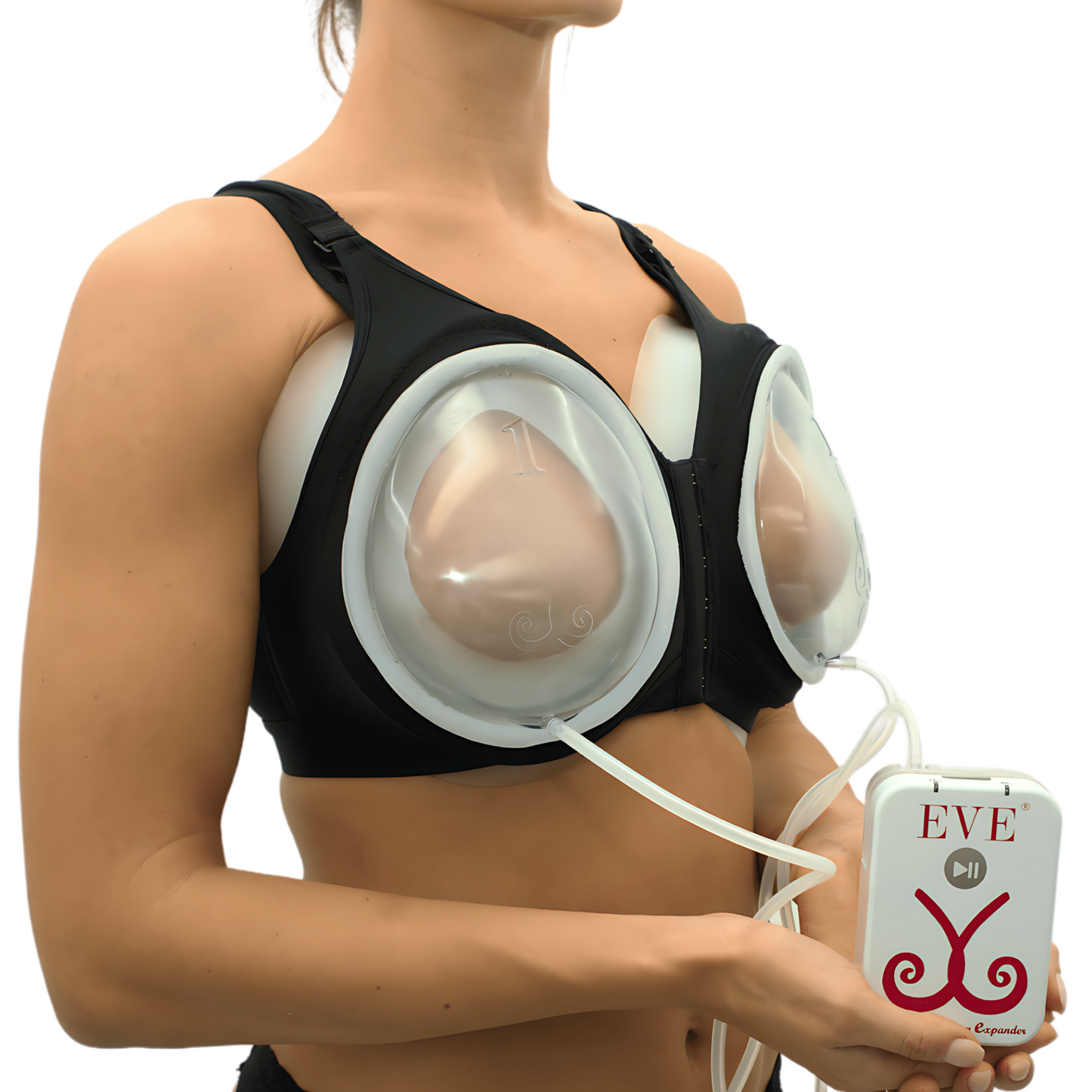
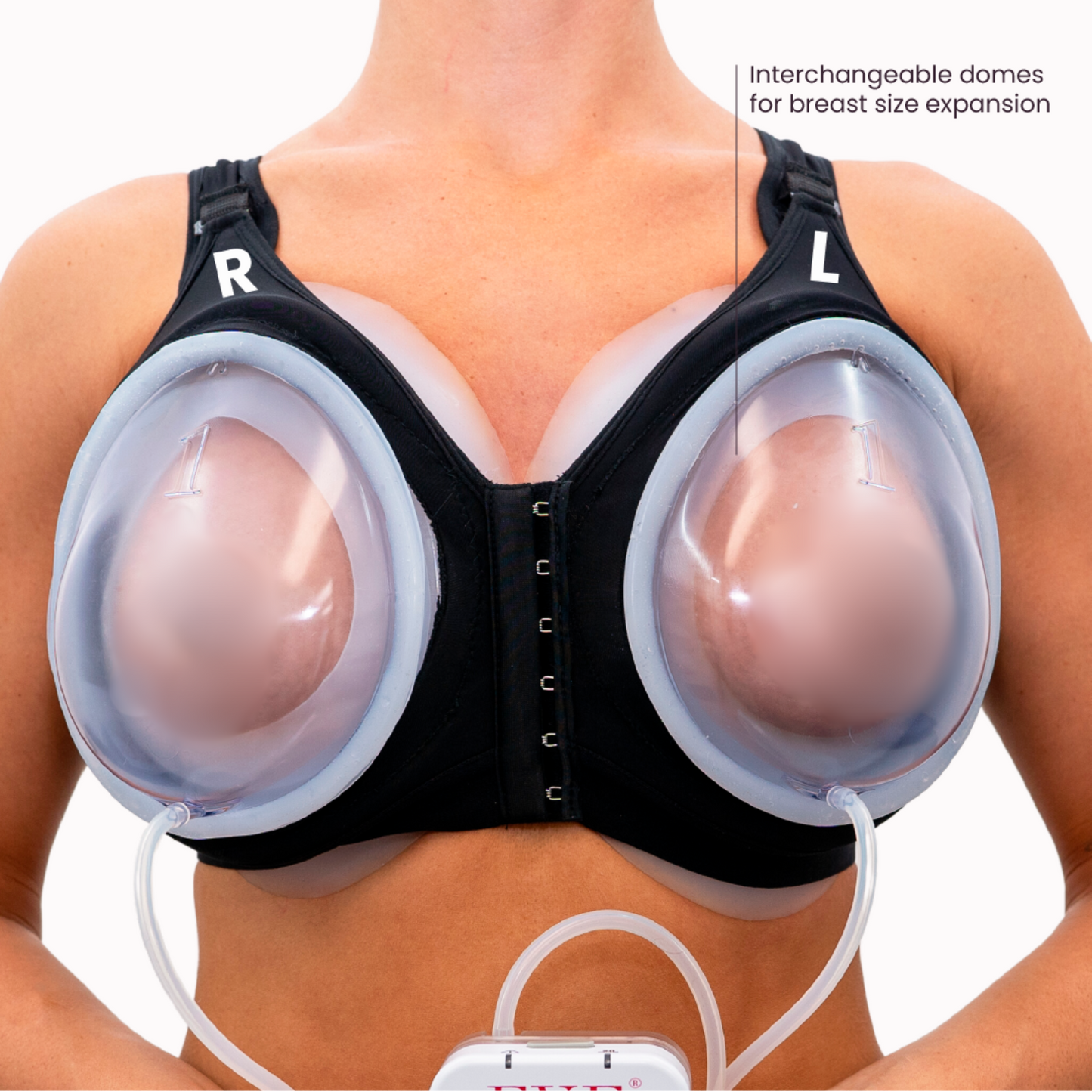
The EVEBRA Device for Natural Breast Growth
EVEBRA is a non-surgical device designed to enhance breast size and shape through the application of mechanical tension. This device is particularly beneficial for transgender women seeking natural breast enhancement either.
Key Features of EVEBRA
-
Non-Invasive Technology: EVEBRA uses gentle, sustained vacuum pressure to stimulate breast tissue growth without surgical intervention.
-
Mechanotransduction: The device works on the principle of mechanotransduction, where mechanical tension promotes cellular proliferation and tissue expansion.
-
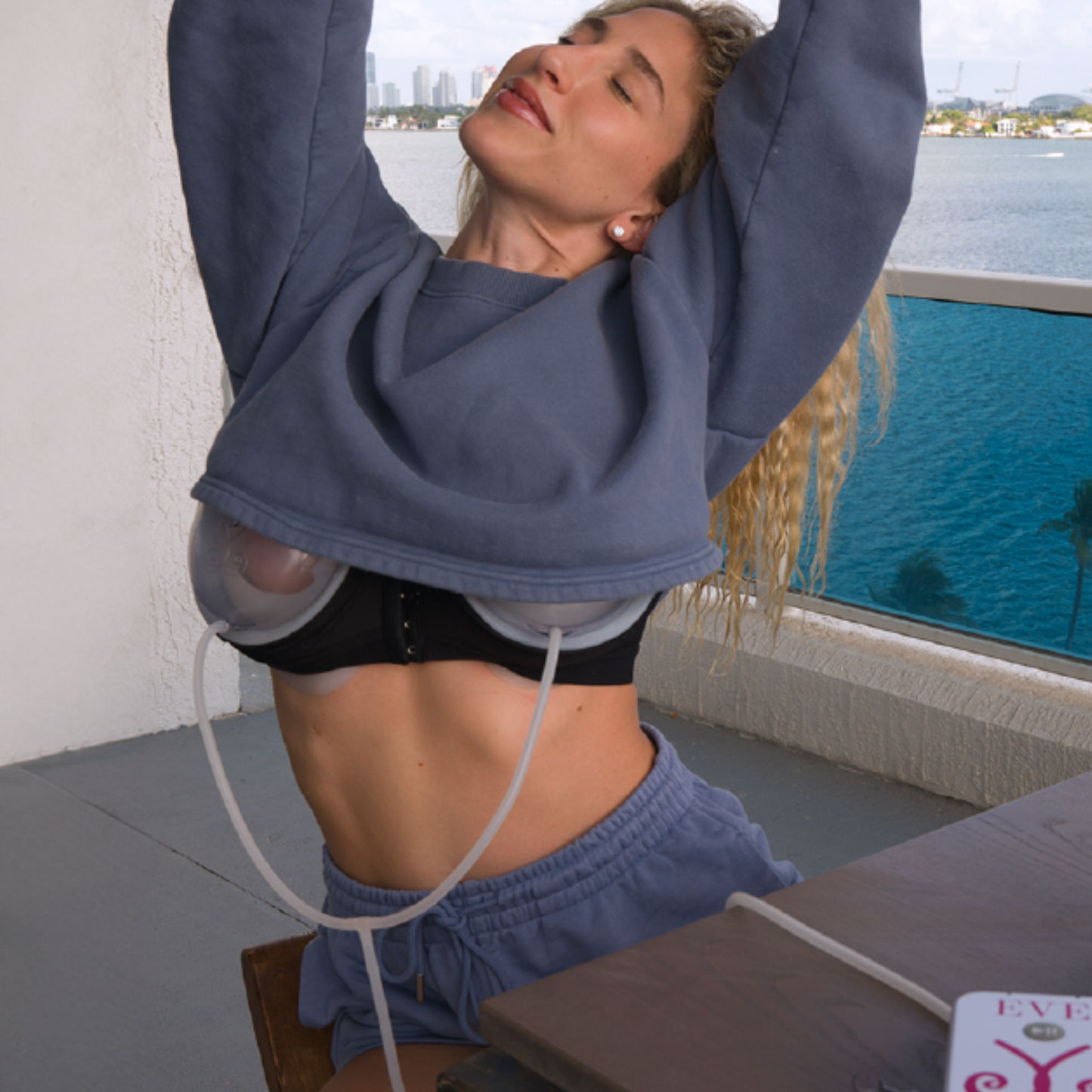
Daily Use: Effective use of the EVEBRA device requires consistent daily application over several months. The device should be worn for at least 10-12 hours daily to achieve optimal results.
-
Clinical Efficacy: Studies have shown significant breast size increase in users of the EVEBRA device, with sustained growth even after discontinuation.
How EVEBRA Works
-
Mechanical Distraction: The device creates a gentle vacuum that stretches the breast tissue.
-
Cellular Response: This mechanical tension activates cellular pathways that lead to tissue growth.
-
Tissue Expansion: Over time, continuous use of the EVEBRA device results in increased breast volume and enhanced shape.
EVEBRA is particularly useful for transgender women with minimal breast tissue growth from hormone therapy alone. It can be used in conjunction with hormone therapy to maximize breast development or as a preparatory step before surgical augmentation.
EVEBRA: An Incredible Option for Male to Female Transformation
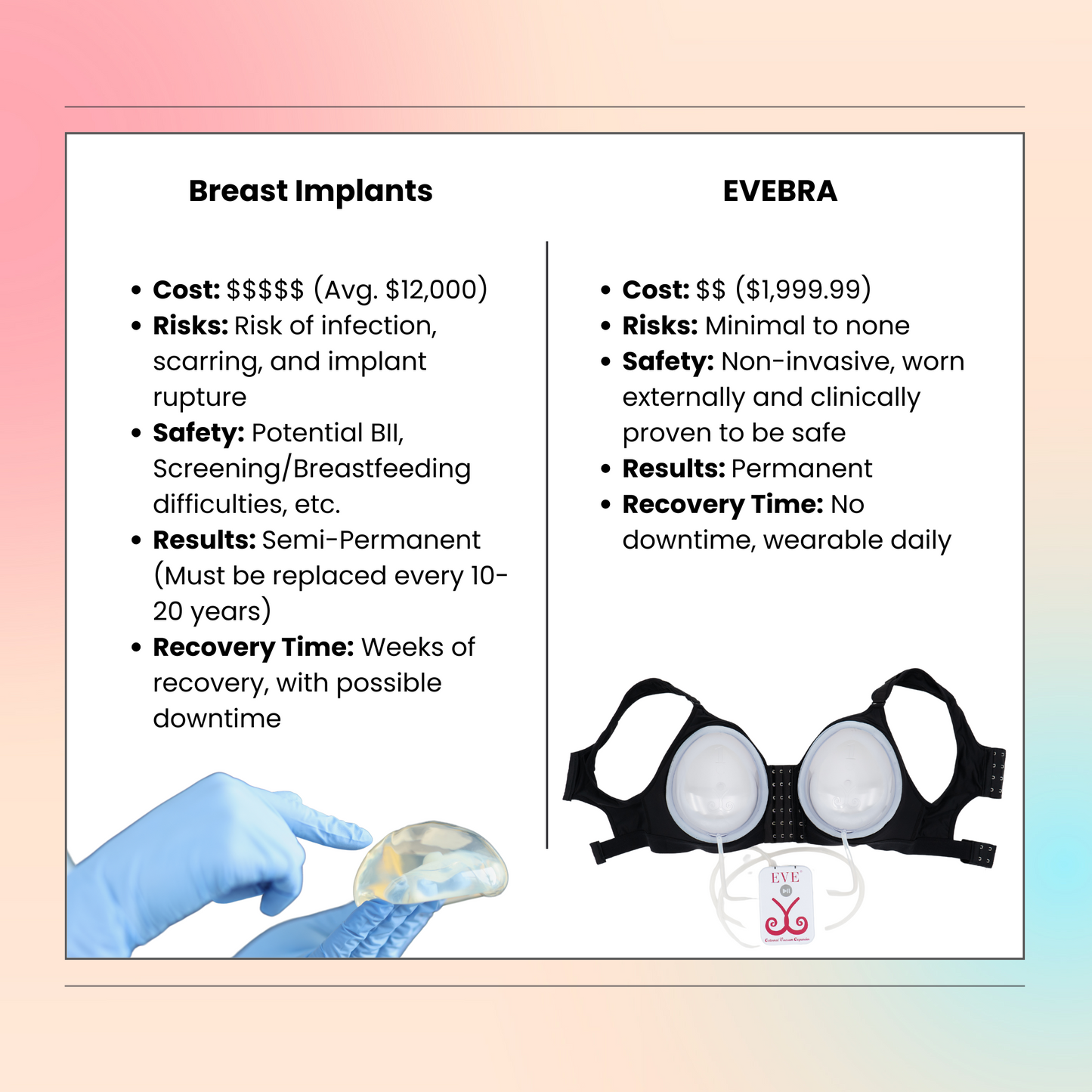
The EVEBRA device stands out as an exceptional option for transgender women seeking non-surgical breast augmentation. Its non-invasive nature makes it an attractive choice for those who may not be ready for surgery or are looking to enhance their results post fat transfer breast augmentation. By providing a natural and gradual enhancement of breast tissue, EVEBRA offers transgender women an opportunity to achieve their desired breast size and shape without the need for immediate surgical intervention. This device also supports the overall gender affirming process, contributing positively to the psychological and emotional well-being of transgender patients by helping them align their physical appearance with their gender identity.
Note: While EVEBRA is an excellent option for non-surgical breast enhancement, it cannot be combined with implant breast augmentation.

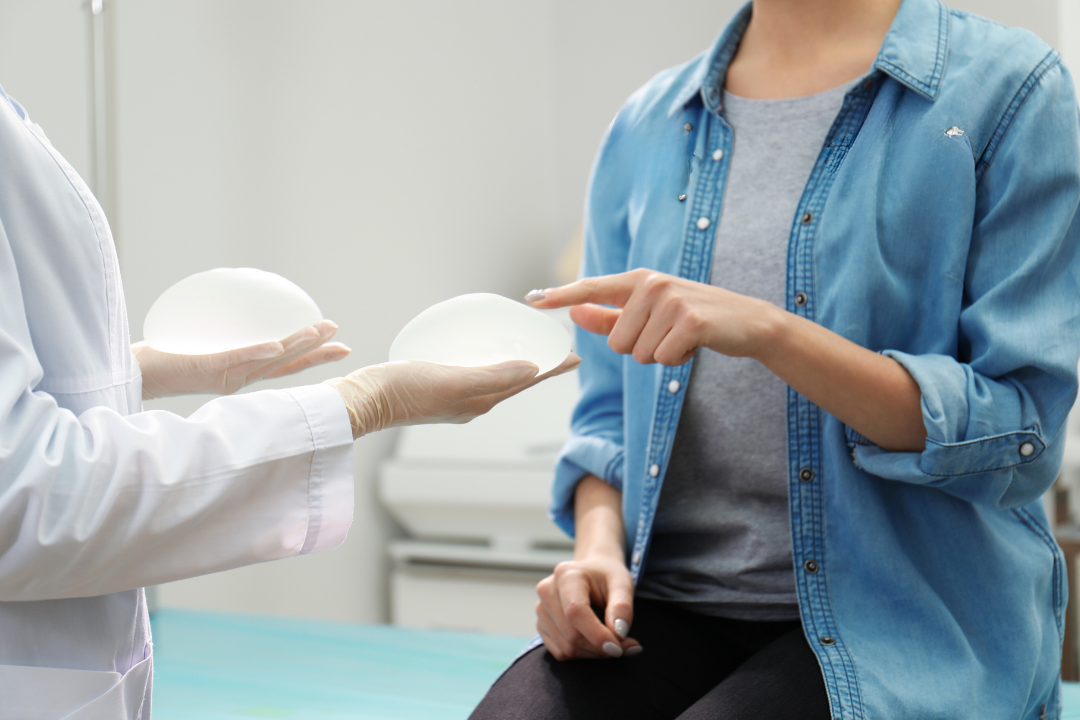
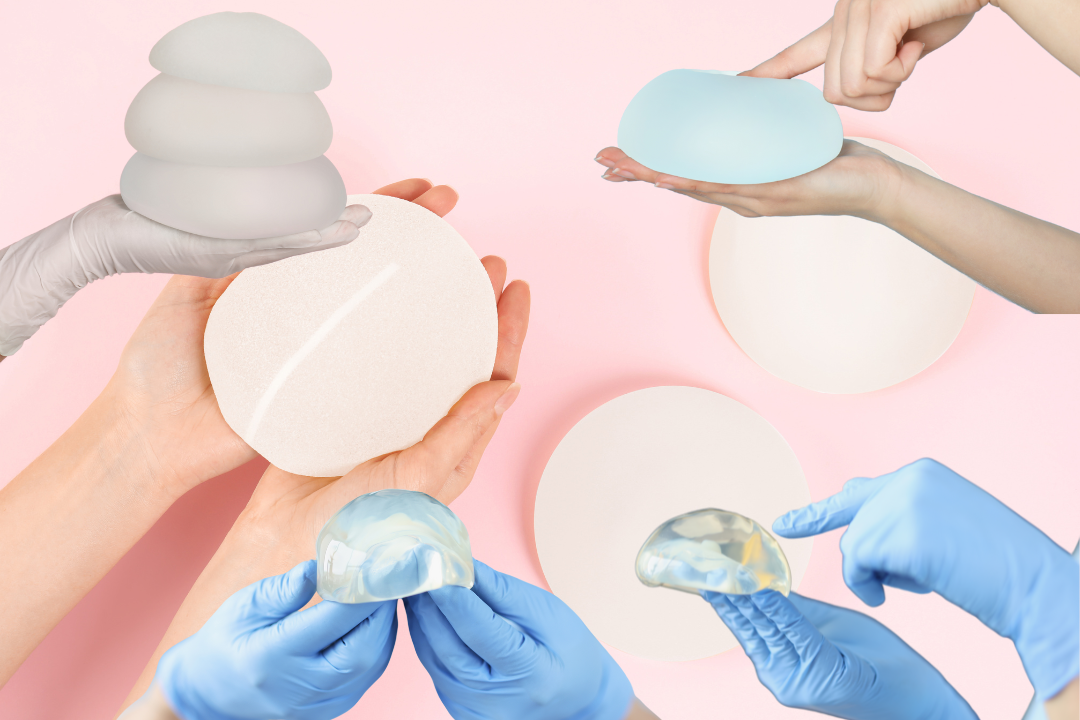
5. Types of Breast Implants For Surgical Breast Augmentation Patients
When considering breast implants, transgender women can choose between silicone and saline implants. Each type has its advantages:
-
Silicone Implants: Known for their natural feel and appearance, silicone breast implants are preferred by many transgender women due to their realistic texture and lower risk of rippling. However, they require a larger incision for placement and can pose a risk of complications such as capsular contracture and rupture.
-
Saline Implants: Easier to adjust in size during surgery and requiring smaller incisions, saline implants offer flexibility, especially for patients with minimal breast tissue. They are filled with sterile saltwater, which the body can absorb safely in case of rupture. Despite these benefits, saline implants might not feel as natural as silicone implants and are more prone to visible rippling, particularly in patients with less natural breast tissue.
Breast Implant Illness
A consideration for plastic surgeons and all patients is the potential for breast implant illness (BII), a term used to describe a range of systemic symptoms that some individuals experience after undergoing breast augmentation with implants. Symptoms of BII can include chronic fatigue, joint pain, and cognitive difficulties. While research on BII is ongoing, and not all plastic surgery patients experience these issues, it is crucial to discuss these potential risks with a qualified plastic surgeon.
Natural Appearance Concerns
For transgender women, achieving a natural appearance is a common goal of breast augmentation. However, there are challenges:
-
Silicone Implants: Although they provide a natural feel, in some cases, the results may still look or feel artificial if there is insufficient natural breast tissue to cover the implants adequately.
-
Saline Implants: These are more likely to show visible rippling and may not feel as natural, particularly in patients with minimal breast tissue, making them less ideal for achieving a natural look.
The choice between silicone and saline implants should be made in consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon who can assess individual needs and anatomical considerations. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients make informed decisions to achieve the best possible outcomes in their gender affirmation journey.

6. Preparing for MTF Breast Augmentation Surgery
Preparation for breast augmentation involves a comprehensive initial consultation. During this phase, the surgeon reviews the patient's medical history, discusses desired breast size, and sets realistic expectations. The patient may also need to undergo certain medical evaluations and mental health assessments.
It is essential for patients to disclose any underlying medical conditions and current medications during the consultation. This information helps the surgeon develop a safe and effective surgical plan. Additionally, patients should discuss their goals and preferences for breast augmentation, including implant size, shape, and incision placement.
7. The Silicone or Saline Implants Surgical Procedure
Breast augmentation surgery typically involves making an incision, creating a pocket under the breast tissue or chest muscle, and placing the implant. The choice of incision location depends on factors such as breast implant, type, desired breast projection, and patient anatomy. Here are the common incision locations:
Inframammary Fold (Under the Breast)
-
Advantages: Favored for its discreet scarring and direct access to the breast pocket, the inframammary fold incision allows precise placement of implants. This method is particularly beneficial for larger implants and provides excellent control over implant positioning.
-
Disadvantages: This approach may leave a visible scar, especially in patients with minimal breast tissue. However, the scar is typically well-concealed in the natural crease under the breast.
Periareolar (Around the Nipple)
-
Advantages: The periareolar incision is suitable for patients with larger areolas. It offers good access for implant placement and allows for concurrent procedures like areola reduction. Scarring blends with the natural pigmentation of the areola, making it less noticeable.
-
Disadvantages: This incision may pose a higher risk of affecting nipple sensation and breastfeeding ability. Additionally, it may not be ideal for very large implants.
Transaxillary (Through the Armpit)
-
Advantages: The transaxillary incision avoids visible scars on the breast itself, placing the scar in the natural crease of the armpit. This approach is preferred by patients who want to avoid breast scarring entirely.
-
Disadvantages: This method can be technically challenging and may offer less precision in implant placement compared to the inframammary approach. It is generally less favored for larger implants due to limited access.
Considerations for Transgender Women
Transgender women often have unique anatomical and technical considerations that can influence the choice of incision location. For instance, patients with minimal breast tissue may benefit from the inframammary approach for better control over implant positioning. Moreover, careful preoperative planning is essential to achieve the desired breast projection and feminine contour.
Surgical Technique and Placement
-
Subglandular Placement: Implants are placed directly behind the breast tissue, offering quicker recovery and more pronounced breast projection. However, this placement may result in more visible implant edges in patients with minimal breast tissue.
-
Submuscular Placement: Implants are positioned beneath the pectoral muscle, providing additional soft tissue coverage and a more natural slope. This placement reduces the risk of capsular contracture and visible rippling, though recovery may be longer and more painful.
Informed Consent and Patient Preparation
Ensuring that patients are well-informed about the surgical procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes is crucial. During the initial consultation, the surgeon will discuss the patient's medical history, perform a physical examination, and use imaging technology to help visualize the results of top surgery. Patients should have realistic expectations and understand the importance of postoperative care to achieve optimal results.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Following breast augmentation surgery, most patients will need to follow specific postoperative care instructions to ensure proper healing and minimize complications. This includes wearing a surgical bra, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments. Pain management, wound care, and monitoring for signs of infection or implant issues are essential components of postoperative care.
By considering these factors and working closely with a qualified plastic surgeon, transgender women can achieve their desired breast size and shape, enhancing their gender affirmation journey and overall quality of life.
8. Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Post-surgery care is crucial for a smooth recovery. Patients are usually advised to wear a surgical bra, avoid strenuous activities, and follow specific wound care instructions. Pain management and monitoring for any signs of complications are also important aspects of post-operative care.
Patients should adhere to their surgeon's recommendations for post-operative care, including attending follow-up appointments and taking prescribed medications. Proper care and rest are vital for minimizing the risk of complications and ensuring optimal healing. Patients should also be aware of signs of infection or implant issues and contact their healthcare provider if any concerns arise.
9. Potential Risks and Complications
Like any major surgery, breast augmentation surgery carries risks such as infection, implant rupture, capsular contracture, and asymmetry. It's essential for patients to be informed about these risks and to maintain regular follow-up appointments with their plastic surgeon.
Capsular contracture, a condition where scar tissue forms around the implant, can cause discomfort and affect breast appearance. Other potential complications include changes in nipple sensation, hematoma, and seroma. By understanding these risks and following post-operative care instructions, patients can reduce the likelihood of adverse outcomes.
10. Achieving Desired Breast Size and Shape
Achieving the desired breast size and shape is a collaborative process between the patient and surgeon. Factors such as body type, existing breast tissue, and personal preferences are taken into account to select the appropriate breast implant size and shape.
During the consultation, the surgeon may use tools such as 3D imaging to help patients visualize potential outcomes. This technology allows patients to make informed decisions about their breast augmentation options. The goal is to achieve a balanced and natural-looking result that aligns with the patient's gender identity and aesthetic desires.

11. Psychological and Emotional Considerations
Breast augmentation can significantly impact a transgender woman's psychological and emotional well-being. It can alleviate gender dysphoria, enhance body image, and improve overall quality of life. It's important for patients to have access to the mental health professional support throughout their transition.
Mental health professionals play a crucial role in supporting transgender patients before and after surgery. Counseling can help patients manage expectations, cope with anxiety, and navigate the emotional aspects of their gender affirmation journey. Ensuring mental health stability is essential for achieving positive surgical outcomes and overall well-being after transgender surgery.

12. Conclusion
Breast augmentation for transgender women is a transformative procedure that significantly impacts their gender affirmation journey. With foundational hormone therapy promoting initial breast tissue growth, patients can choose between surgical and non-surgical options like EVEBRA for enhancement. Advanced surgical techniques, including submuscular implant placement and precise incision choices, help achieve natural-looking results. Comprehensive postoperative care and mental health support are crucial for successful recovery. High patient satisfaction rates are achieved through thorough planning, expert execution, and realistic expectations, ultimately enhancing both physical appearance and emotional well-being.